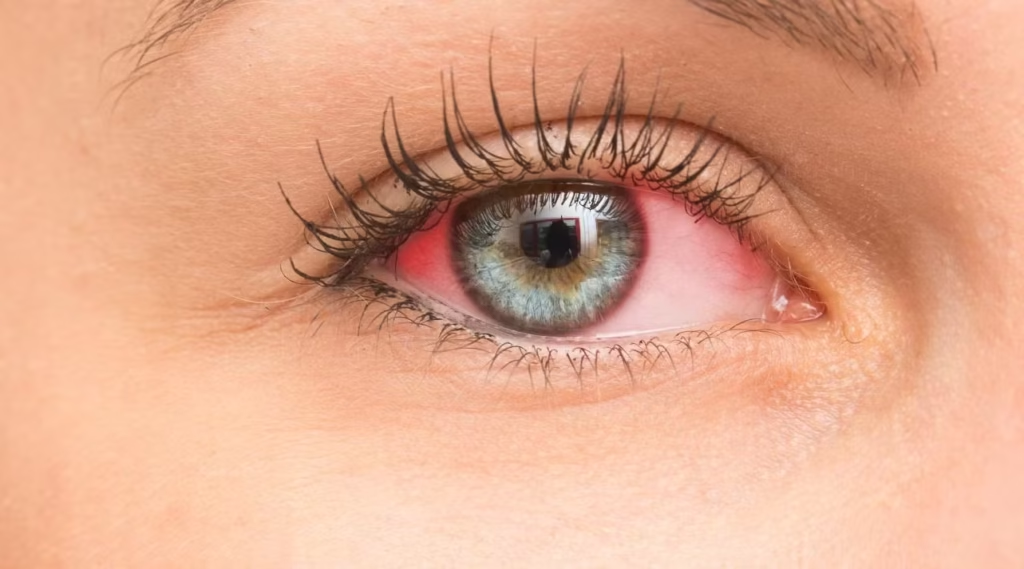
Pink Eye: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Pink eye, or conjunctivitis, is the most common eye infection affecting both children and adults. It is characterized by a red, mildly irritated eye and can be highly contagious. Fortunately, pink eye is easily treatable and typically does not cause long-term damage to the eye.
Causes of Pink Eye
Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the conjunctiva, the clear membrane that covers the whites of the eyes and the inner surfaces of the eyelids. The condition can be caused by:
1. Bacterial Conjunctivitis
- Caused by staphylococcal or streptococcal bacteria from the skin or respiratory system.
- Spread through contact with contaminated surfaces or use of contaminated eye makeup.
2. Viral Conjunctivitis
- Caused by viruses like adenoviruses, often associated with the common cold.
- Spread through exposure to respiratory droplets from coughing or sneezing or via the mucous membranes connecting the respiratory system and eyes.
3. Allergic Conjunctivitis
- Triggered by exposure to allergens such as pollen, pet dander, or dust.
- Causes redness, swelling, and itching.
4. Chemical Conjunctivitis
- Results from exposure to air pollutants or chemicals, such as chlorine in swimming pools.
- Can lead to irritation and inflammation.
Symptoms of Pink Eye
The symptoms of conjunctivitis vary depending on its cause:
Viral Conjunctivitis
- Clear, watery discharge
- Diffuse redness in the eye
- Gritty, scratchy, or burning sensation
- Swollen eyelids
- Tender lymph nodes in front of the ears
Bacterial Conjunctivitis
- Thick, mucus-like discharge, especially after sleep, which may glue the eyes shut
- Redness and irritation
- No tenderness of lymph nodes
Allergic Conjunctivitis
- Watery discharge
- Intense itching
- Swelling of the conjunctiva (chemosis), sometimes causing the white of the eye to appear bulging
Treatments for Pink Eye
The treatment approach for conjunctivitis depends on the underlying cause.
Viral Conjunctivitis
- Cannot be treated with topical medications—must run its course (up to two weeks).
- Symptom relief:
- Cool compresses
- Artificial tears
- In some cases, topical steroids may be prescribed for discomfort, though they do not shorten the infection’s duration.
Bacterial Conjunctivitis
- Treated with topical antibiotic eye drops.
- Symptoms often improve quickly, but the drops should be used for up to 10 days to prevent recurrence.
Allergic Conjunctivitis
- Avoid exposure to the allergen.
- Mild reactions: Cold compresses and artificial tears.
- Severe reactions:
- Topical antihistamine drops
- Topical NSAIDs or steroids
- Oral antihistamines, if needed
Chemical Conjunctivitis
- Immediate flushing of the eye with saline to remove the irritant.
- Acute chemical injuries require emergency medical attention to prevent scarring or vision loss.
Preventing the Spread of Infectious Pink Eye
To avoid transmitting bacterial or viral conjunctivitis:
- Wash hands frequently.
- Avoid touching your eyes.
- Do not share towels or personal items.
When to Seek Professional Help
If you experience symptoms of conjunctivitis or have concerns about your eyes, schedule an appointment with a Doctor of Optometry. Alberta Health Care covers the cost of medically necessary visits for conditions like conjunctivitis.
At The Optometrists’ Clinic Inc., our team is here to help. With five convenient locations, we offer care and advice tailored to your needs.
For more information or to book an appointment, contact us today. We’re happy to assist you with any questions or concerns about pink eye!